As ecommerce continues to grow, delivery speed has become just as important as price and product quality. This shift is clearly visible in the rapid rise of quick-commerce platforms such as Zepto, Blinkit, Flipkart Minutes, Swiggy Instamart, and BigBasket Now.
Rapid urbanization and the expansion of local businesses have further accelerated demand for instant fulfilment. Today, nearly 77% of consumers expect their orders to be delivered within two hours, pushing ecommerce brands to invest in hyperlocal fulfilment centers and faster delivery models.
This shift has led to the rise of hyperlocal delivery, a logistics model built around short distances, nearby vendors, and rapid delivery timelines to serve neighborhood-level demand. While often confused with last-mile delivery, hyperlocal fulfilment follows a fundamentally different operating logic.
In this blog, we will explain the hyperlocal delivery meaning, clarify what hyperlocal delivery is, explore hyperlocal delivery in ecommerce, and compare it with last-mile delivery to help brands choose the right fulfilment approach.
Psychometric Changes in Consumer Behavior Fueling Hyperlocal Delivery
Earlier, waiting 3–5 days for an online delivery was considered acceptable. Today, even a short delay in receiving daily essentials triggers dissatisfaction and doubt. This fundamental shift in consumer perception, from planned purchasing to instant gratification, has redefined ecommerce fulfilment expectations.
Rising smartphone usage, on-demand platforms, and quick-commerce experiences have conditioned consumers to expect near-instant deliveries, especially for high-frequency products. As a result, traditional fulfilment models have struggled to keep pace, paving the way for hyperlocal delivery as a natural response to evolving consumer psychometric behavior.
What is Hyperlocal Delivery?
It is an on-demand delivery model where products are picked up from local merchants or sellers and delivered to customers within a limited geographical boundary, usually within 2–8 hours.
The popularity of hyperlocal delivery is driven by:
- Faster delivery expectations
- Urban density and smartphone penetration
- Growth of grocery, food, and medicine ecommerce
- Technology-led logistics platforms
The key USP of hyperlocal delivery lies in geographical proximity and rapid delivery timelines.
Key Features of the Hyperlocal Delivery Model
The hyperlocal delivery model has distinct operational characteristics:
1. Restricted service area: Deliveries are limited to a small radius, typically 5–15 km.
2. Urban demand focus: Most hyperlocal operations are centered around high-density urban and semi-urban pockets.
3. Technology-driven ecosystem: It relies on automation across:
- Ecommerce platforms
- Logistics partners
- Local vendor systems
4. Speed as the primary value proposition: Delivery timelines range from 2–3 hours, with a maximum of 6–8 hours.
5. Local ecosystem enablement: The model builds an ecosystem connecting consumers, local vendors, aggregators, and delivery partners, contributing to local economic upliftment.
How Hyperlocal Delivery Works for Ecommerce Companies
In hyperlocal delivery in ecommerce, fulfilment happens through close collaboration between logistics companies and local vendors.
1. Typical Order Flow:
- The consumer places an order via a mobile app or ecommerce platform.
- The nearest local vendor receives and accepts the order.
- A delivery agent picks up the package from the vendor location.
- The order is delivered directly to the customer within the defined radius.
2. Aggregator-Based Hyperlocal Delivery Model
Most hyperlocal businesses operate on an aggregator model, where the platform acts as a bridge between vendors and consumers.
In this setup:
- The aggregator manages technology, routing, and delivery allocation.
- Vendors focus on inventory and order preparation.
- Delivery agents ensure fast local fulfilment.
This model allows ecommerce companies to scale hyperlocal delivery without owning inventory or delivery fleets.
3. Hyperlocal Delivery Model Explained
The hyperlocal delivery model is an on-demand logistics service designed to deliver goods within a small geographical area using a centralized technology platform.
Its core strengths are:
- Defined delivery radius
- Ultra-fast delivery timelines
- Localized supply sourcing
- Asset-light operations
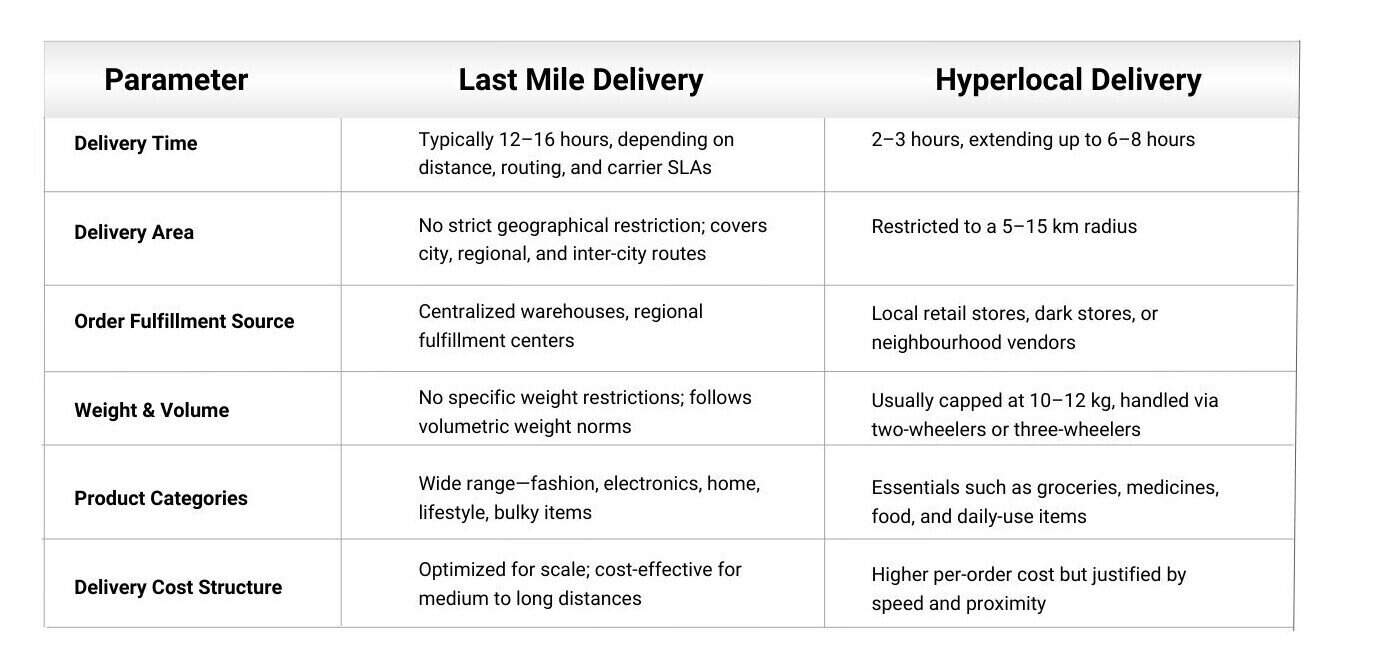
Hyperlocal Delivery vs Last Mile Delivery
While both hyperlocal delivery and last-mile delivery aim to get products to customers efficiently, their execution differs significantly.
Hyperlocal Delivery vs Last Mile Delivery: Detailed Comparison
When Should Ecommerce Brands Use Hyperlocal Delivery?
Hyperlocal delivery in ecommerce works best when:
- Speed is critical to conversion
- Products are locally available
- Order frequency is high
- Delivery density is concentrated
It is especially effective for grocery, pharma, food delivery, and quick-commerce use cases.
Future of Hyperlocal Delivery
The future of hyperlocal delivery is expected to expand beyond urban convenience into broader supply chains:
- Expansion into rural and semi-urban markets
- Ecommerce giants building hyperlocal ecosystems
- Growth of micro-warehousing and dark stores
- Increased use of AI in local retail demand forecasting
- Emergence of air delivery drones for short-distance fulfilment
- Gradual adoption of blockchain in distribution and traceability
Final Thoughts
While last-mile delivery remains essential for large-scale ecommerce fulfilment, hyperlocal delivery is redefining speed-led commerce by bringing products closer to consumers than ever before.
For ecommerce brands looking to win on speed, convenience, and local relevance, hyperlocal delivery is no longer optional; it has become a strategic advantage.
Platforms like Shipway enable brands to operationalize hyperlocal delivery at scale by providing carrier integrations, real-time shipment visibility, SLA monitoring, and automated delivery workflows. By connecting ecommerce platforms with local delivery partners and enabling faster issue resolution, Shipway helps brands maintain a consistent customer experience even in high-frequency, short-radius deliveries.
What does ecommerce fulfilment mean?
Ecommerce fulfilment covers the entire process from order placement to final delivery, including inventory management, packing, shipping, and returns. A reliable online courier service plays a key role in ensuring orders reach customers on time and in good condition.
What is the hyperlocal delivery meaning in ecommerce?
The hyperlocal delivery meaning in ecommerce refers to fulfilling online orders using local supply sources instead of centralized warehouses. This allows ecommerce brands to deliver faster by serving customers within a 5–15 km radius, making it ideal for essentials and quick-commerce use cases.
How is hyperlocal delivery different from last-mile delivery?
While both aim to deliver orders to customers, last-mile delivery typically covers longer distances from regional warehouses and takes 12–16 hours. Hyperlocal delivery, on the other hand, operates within a limited radius and focuses on same-hour or same-day delivery, often within 2–3 hours.
When should ecommerce brands use hyperlocal delivery in ecommerce?
Hyperlocal delivery in ecommerce works best when speed directly impacts conversions, products are locally available, and order frequency is high. It is especially effective for grocery, pharma, food delivery, and quick-commerce brands serving dense urban areas.
What types of products are best suited for hyperlocal delivery?
Hyperlocal delivery is best suited for high-frequency and essential products such as groceries, medicines, food items, tiffin services, and daily-use goods. These categories benefit the most from shorter delivery timelines and proximity-based fulfilment.
How can ecommerce brands manage hyperlocal delivery at scale?
Ecommerce brands can manage hyperlocal delivery efficiently using logistics platforms like Shipway, which provide carrier integrations, real-time shipment tracking, SLA monitoring, and automated delivery workflows. Such platforms help maintain consistency and visibility even across multiple local delivery partners.

